Table of Contents
Have you ever felt like finance is just a big jumble of confusing words? Well, you’re not alone! Three terms that often leave people scratching their heads are Face Value, Book Value, and Market Value. It’s like trying to figure out the difference between identical triplets!
Let’s break it down.
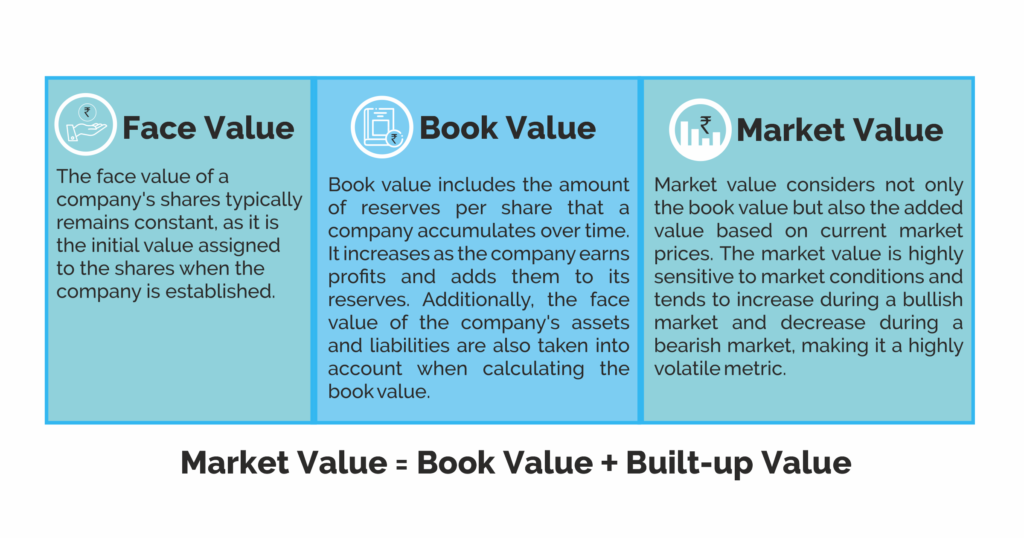
Face Value is like the sticker price on a car – it’s the value of a stock as listed by the company. Think of it like the stock’s starting point.
Now, Book Value is like a secret code that only financial detectives can decipher. It’s the value of the company’s assets minus its liabilities. In other words, it’s like the company’s net worth. Book Value can help you figure out if a stock is overpriced or a steal of a deal.
And last but not least, Market Value is like the stock’s popularity contest. It’s the value of the stock as determined by the market, based on supply and demand. It’s like the stock’s current value in the eyes of investors.
So, can these terms be used interchangeably? Absolutely not! They’re like different colors of the rainbow – each one is unique and important in its own way. Understanding the difference between these terms can help you make smarter investment decisions and pick better stocks. So, it’s time to start decoding these finance terms like a pro!
What is Face Value(FV)?
Face Value is the nominal value or par value of the stock at the time of issuing. It is the value of a company’s common stock on the balance sheet and is determined during the initial stages of the offering. It can be termed as the original cost of the stock. It does not denote the actual market value.
The FV of a stock does not fluctuate and undergoes changes if the company goes in for a stock split or reverse stock split. The stock is split keeping in mind the face value and not market value. For instance, if the stock’s face value is Rs 10, and there is a 1:2 split, its face value will change to Rs 2. Accordingly, market value also gets adjusted.
The dividend is usually quoted per share or as a percentage of the face value of the share and not on market value. For instance, if a company declares a dividend of 100% with a face value of Rs 10, then the dividend amount will be Rs 10 per share. Thus, it is always in the interest of the investors to look at the dividend amount and not dividend percentage.
Face Value is calculated using two important numbers: (i) Equity share capital (ii) Number of shares outstanding.
Face Value = Equity share capital / Number of shares outstanding
Thus, face value is nothing but Equity Share Capital per share. It is a static theoretical number.
What is Book Value(BV)?
Book value literally means the value of a business according to its books (accounts) that is reflected through its financial statements or its net worth. Theoretically, it represents the total amount a company is worth if all its assets are sold and all the liabilities are paid back. In other words, it reflects the firm’s Free equity. Fluctuation in Book Value is infrequent and changes annually, as per business performance.
BV can be helpful in determining whether the company’s stock is overvalued, undervalued or fairly valued. One must note that if the company is having a component of minority interest that is profit in the books because of any sister concern under it, that value must be further deducted to arrive at the right book value.
Book Value can be calculated in two ways:
(i) Book Value = Total Assets – (Total Liabilities – Current Liabilities)
(ii) Book Value per share = Face Value + Reserve per share
The second formula establishes a relationship between Book Value and Face Value.
Few issues with book value are that the figure is reported at an annual frequency. It is only after the reporting that an investor would know how the company’s book value has changed over time. It is an accounting item and is subject to adjustments which may not be easy to understand and assess. For the calculation of book value, only tangible assets are taken into consideration so it is not very useful for businesses relying heavily on human capital.
See also: Book Value Per Share
What is Market Value(MV)?
Market Value is the current price of the stock quoted on exchange and may or may not reflect the fair value of the stock. It represents the company’s worth. MV constantly changes with the movement in the stock market. In the short term it will change every moment as per the whims of the market sentiment and in the long term, it is driven by business performance. It is the market price of the stock at which we buy or sell the stock. Hence, this is the most important data when it comes to stock trading. Market Value of a company is calculated as:
Market Value = Current Stock Price * Number of shares outstanding
MV is also known as Market Capitalization.
Market value considers both tangible as well as intangible assets. However, the basis of market value is not definite. There are n numbers of factors that influence the market value of a company like profitability, performance, liquidity or even simple news which can increase or decrease its market value. Thus, one can say that the market value of a company reflects its current trend.
The relationship between market value, face value, and book value:
Comparing Book Value and Market Value
Book Value and Market Value are compared by investors to determine whether the stock is overvalued, undervalued or fairly valued.
(i) Market Value is lesser than Book Value: This indicates that the market is not confident about the company’s prospects. In other words, the market feels that the company is not worth the value of its books or there may not be enough future earnings. However, Value Investors look out for such companies as they feel that they are undervalued and the market is wrong about their valuation.
(ii) Market value greater than book value: This indicates that the market is assigning a higher value to the company and its assets. In other words, investors believe that the company has excellent future prospects for growth, expansion and increased profits that eventually can raise the book value of the company. Growth investors may find such companies promising. However, it may also include overvalued or overbought stocks which are already trading at a high price.
(iii) Market value equals book value: This indicates that the market sees no compelling reason to believe the company’s assets are better or worse than what is stated on the balance sheet. In other words, that market finds the company to be fairly valued.
StockEdge App
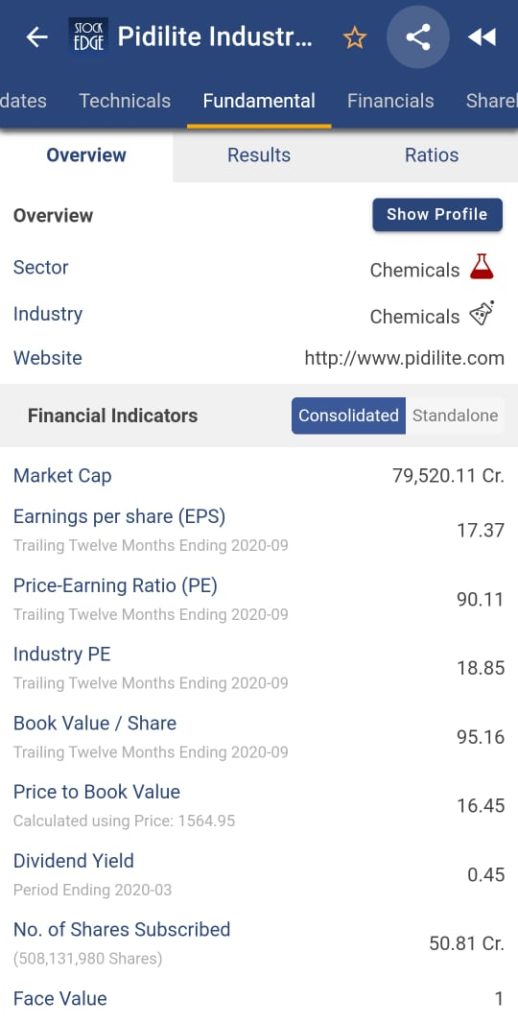
With StockEdge app we don’t have to calculate Face Value, Book Value and Market Value of any stock. It is readily available in this APP.
Suppose we want to look at the Face value, Book value and Market Value of Pidilite Industries Limited. First, click on the Fundamental tab and under the overview section we will get all the above-mentioned values for the stock.
Check out our interesting features at StockEdge Web Version.
Bottom line
The face value of the share is least meaningful for the investor and its value is used just for bookkeeping purpose. However, book value and market value help in the determination of market sentiments for the company and provide meaningful insights into a company’s valuation. Comparing the book value to the market value of a company helps investors to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued given its assets, liabilities and its ability to generate income.