Table of Contents
“Markets are never wrong, but options are” by Jesse Livermore.
Options trading is a game of high risk-high reward. It is a double-edged sword where your probability of winning a trade matters the most. Regardless of the market scenario and despite all odds, you can equally make profits or losses. Yes, OPTIONs can give you a lot of options in trading, but only choosing the right option at the right time can increase your probability of making a handsome profit in option trading.
If all these seem somewhat complex to you, in this blog, we will explain the very basics of options trading and provide a comprehensive guide on how you can start trading in options as a beginner trader.
The Basics of Options Trading
Before explaining the basics of options trading? It is essential to understand what the options are exactly. They are financial contracts between a buyer and seller where the buyer of an option has the right, not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset. In contrast, the option seller has an obligation to fulfill the contract.
Options trading is a part of the Futures and options (F&O) segment of the stock market, commonly referred to as the Derivatives market.
Options trading allows you to make predictions about the future price movements of an underlying asset. Basically, underlying assets can be stocks, commodities, currencies, etc.
Defining Options Trading
Options trading, as mentioned earlier, is a process of buying and selling option contracts of a particular underlying asset. You, being a buyer of an option, have the right but no obligation to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. On the other hand, if you are the seller of an option, you have an obligation to honor the contract if the buyer wishes to exercise the rights.
With options, you can capitalize on market movements without owning the actual underlying asset. This approach allows you to leverage your investment capital, potentially leading to higher returns with higher risk; at its core, option trading centers around speculating on the future price movement of the underlying asset.
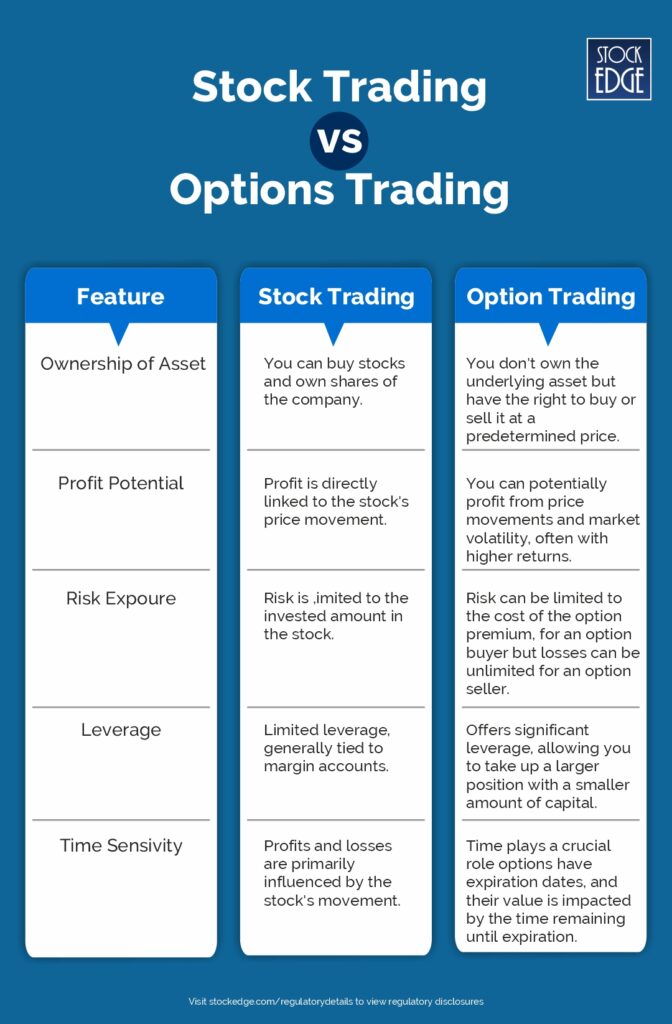
Differentiating Options from Other Trading Instruments
For a beginner in options trading, it may seem different from your conventional stock trading. While you are trading in stocks and buying shares of a company means you actually own the underlying asset, which is the shares of a company, whereas options are basically a financial contract that provides you with an option whether you want to buy the stock at a predetermined price at a later date. However, it is important to note that the value of the option contracts, which is essentially the premium of the option, is derived from the underlying asset. Hence, they are known as derivative contracts.
The Mechanics of Options Trading
Options trading basically involves the buying and selling of financial contracts known as options. An option contract specifies the type of option, its specific price, the expiration date, and the underlying asset, which could be stock, commodity or currency.
How Options Trading Works?
In options trading, transactions occur between a buyer and a seller of an option contract. The buyer pays a premium to get the privilege of buying or selling the asset at a predetermined price on or before the expiry date. Conversely, the seller, who receives the premium from the buyer, is obligated to provide the asset or take delivery of the asset, as the case may be if the buyer chooses to exercise the option.
One important thing to note is that options trading is a zero-sum game between the buyer and seller of options. “One’s profit is another’s loss.”
Understanding Options Contracts
An option contract is based upon the underlying asset, as the value of the option is derived from it. The contract also specifies the price at which the contract may be exercised on or before it expires.
Now, the value of the option contract which is essentially the premium that changes based on the underlying asset price movements. On the other hand, the expiry date of the option contract represents the future date by which the option must be exercised, or it becomes worthless.
Types of Options
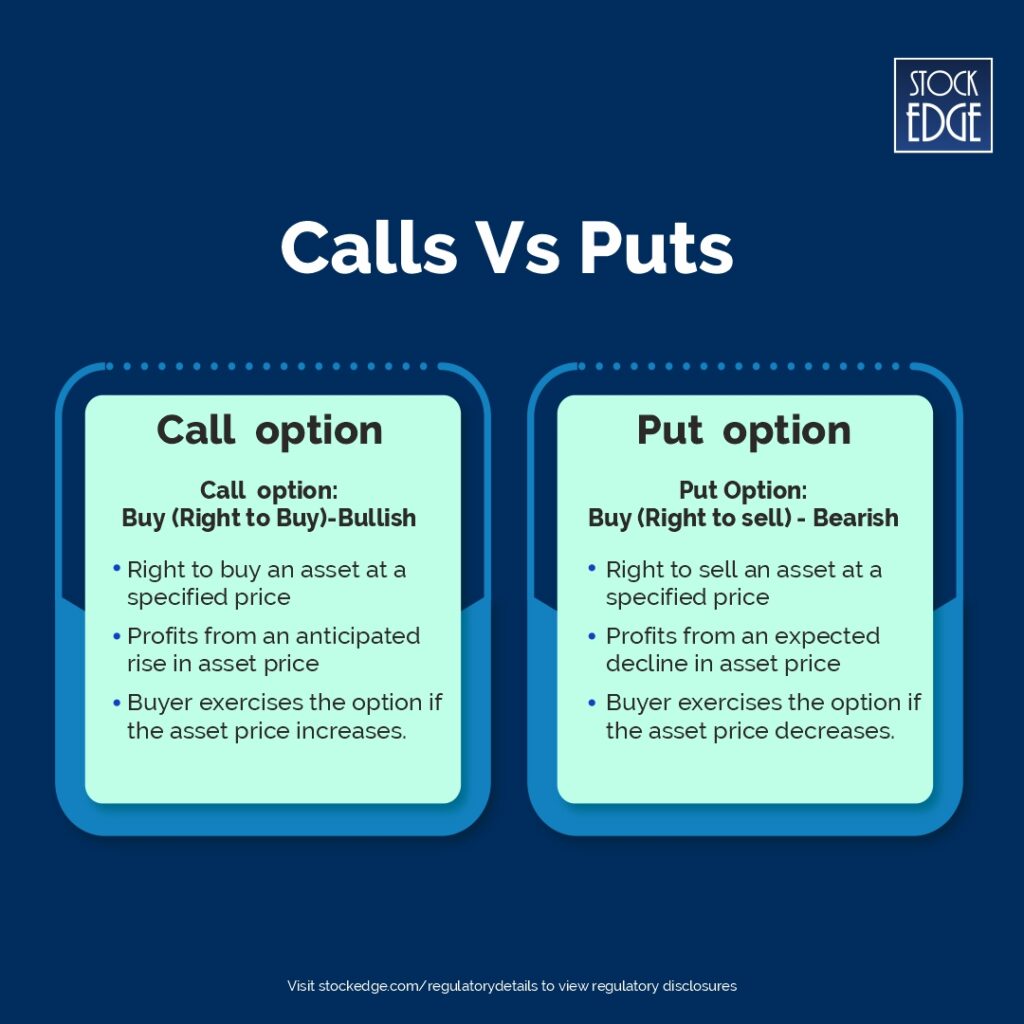
Options are basically of two types: Call & Put
Call Option
A call option offers the (buyer) the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before the contract expires.
For instance, if you are a call buyer, it means you anticipate that the price of the underlying asset will rise. If the price indeed increases, the call option can be exercised, allowing you to buy the asset at a lower, which is the agreed-upon price.
To give you a practical example, suppose that the stock price of SBI is currently at 600 per share, and you enter into a call option contract with the seller and agree to buy 3000 shares after 26 days. Meanwhile, the stock price of SBI increased to 670 per share, which means that even if the market price of SBI is at 670, you can still buy at 600 per share.
Put Option
A put option offers the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before the contract expires.
For instance, if you are the buyer of a put option, you are expecting the price of the underlying asset to fall. If the price decreases, the put option can be exercised, allowing you to sell the asset at a higher price, which is the agreed-upon price.
To give you a practical example, suppose you are holding shares of ITC Ltd., which is currently trading at 430 per share. You are expecting that the stock price may fall in the near future. Therefore, you bought a Put option contract, giving you the right to sell your shares of ITC at 430 per share. Meanwhile, the share price dropped to 400 per share, but as a buyer of the Put option, you can sell your shares at the aggregate price, which is 430 per share.
Please note that the above examples are given based on the point of view of the buyer of an option contract. Conversely, the option seller, in terms of call or put, has an obligation to honor the contract if the buyer wishes to exercise it. This means a call seller has to deliver the asset, while the put seller has to take delivery of the asset. Being an option seller, you receive the option premium but may be obligated to fulfill the terms of the option if the buyer decides to exercise.
Key Terms in Options Trading
Options trading involves a unique set of terms that you must understand to navigate the complexities of the derivatives market effectively, especially options. Some of the important ones to note are:
- Underlying Asset
The financial instrument (e.g., stocks, indices, commodities) on which the option contract derives its value. - Strike Price
The pre-agreed price at which the underlying asset can be bought (for a call) or sold (for a put) before or at expiration. - Expiration Date
The expiration date is when the option contract ends, and it’s no longer valid. - Option Premium
The premium is the price the option buyer pays to the seller, and it’s what the option contract costs. - Lot Size
Lot size in stock options refers to the predefined quantity of shares or units in a single option contract, you have to trade.
Steps to Get Started With Trading In Options In India
Starting to trade options in India? Understand the basics from our blog. Know the different options like stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies—these are the financial instruments you can trade.
To start with, choose any particular underlying asset. Be it index or stock options. Define your risk-reward ratio before entering into any option trades. Keep developing strategies based on your risk appetite. If you are relatively new, you can even start with paper trading and then deploy real money on the strategies you have developed. This comprehensive approach ensures a well-informed and strategic entry & exit in the realm of options trading in the Indian market.
Setting Up a Trading Account
Setting up a trading account for options trading in India involves several vital steps to ensure a smooth and informed entry into the derivatives market.
- Choose a broker: Do proper research and choose a broker that supports Futures and options trading. Please note that not all brokers in India allow F&O trading to their clients. Additionally, consider factors such as brokerage fees, user interface, research tools, and customer support.
- Complete KYC: You must complete the Know Your Customer (KYC) process by providing the necessary documents, including proof of identity, address, and PAN card, along with your income proof. Yes, to trade in the f&o segment, it is mandatory to disclose your proof of income.
- Link your Bank account: Once you have opened your trading account, link it with your bank account. This facilitates the seamless transfer of funds for trading and withdrawing profits.
Now, you are good to go with your option trading journey.
Analyze Stock options using StockEdge
If you’re thinking about which stocks to pick for options trading, remember that not all stocks are in the Futures & Options (FnO) segment. Currently, there are only 183 stocks listed in the FnO segment.
You can download the list of all f&o stocks from the NSE website.
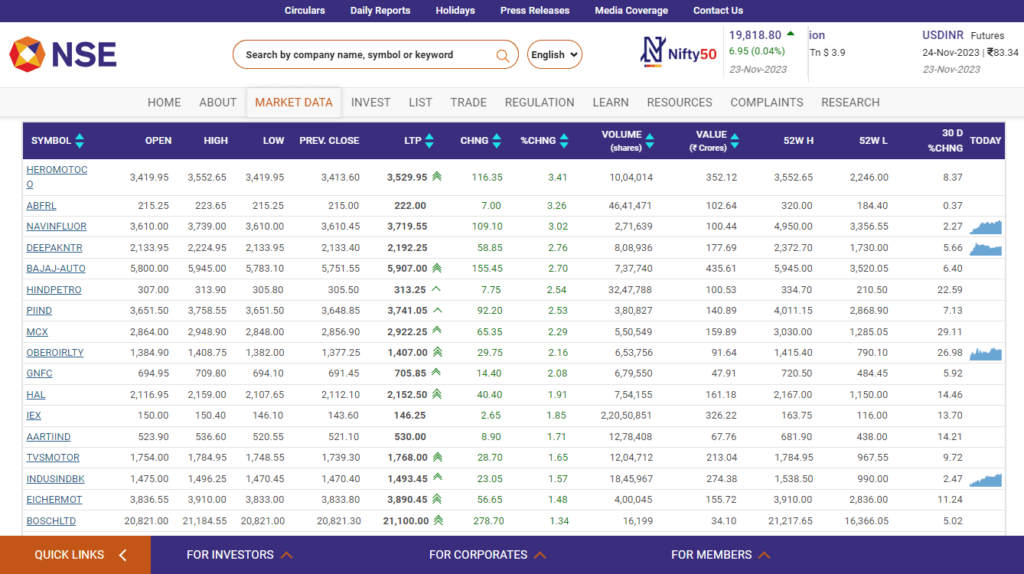
But out of 183 stocks, how can you understand which stocks are bullish or bearish? That’s where StockEdge can help you out. We have a section called “Derivatives Analytics”
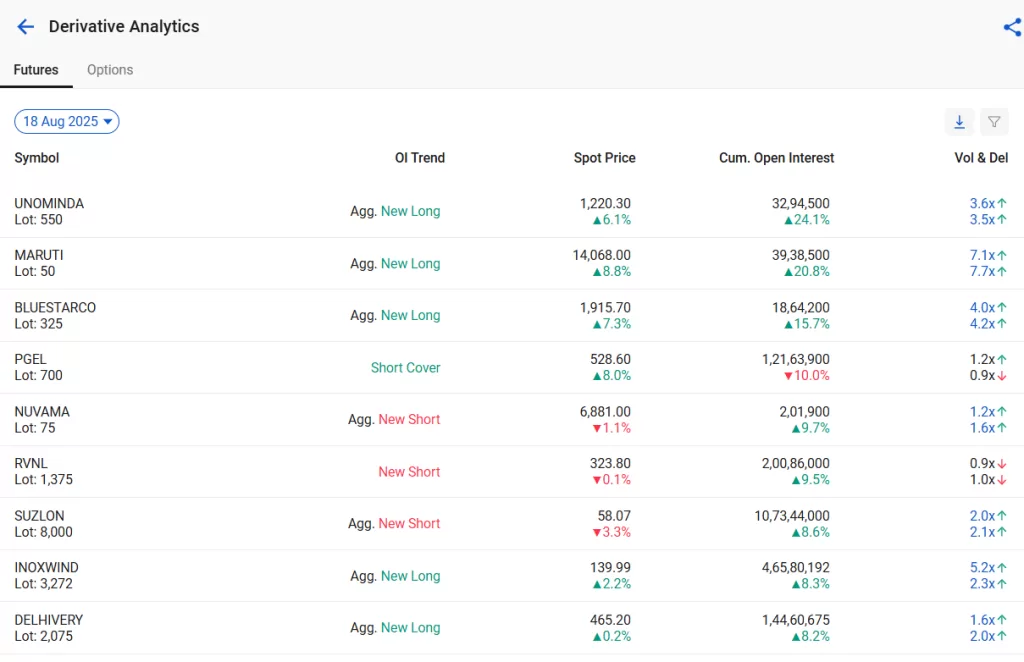
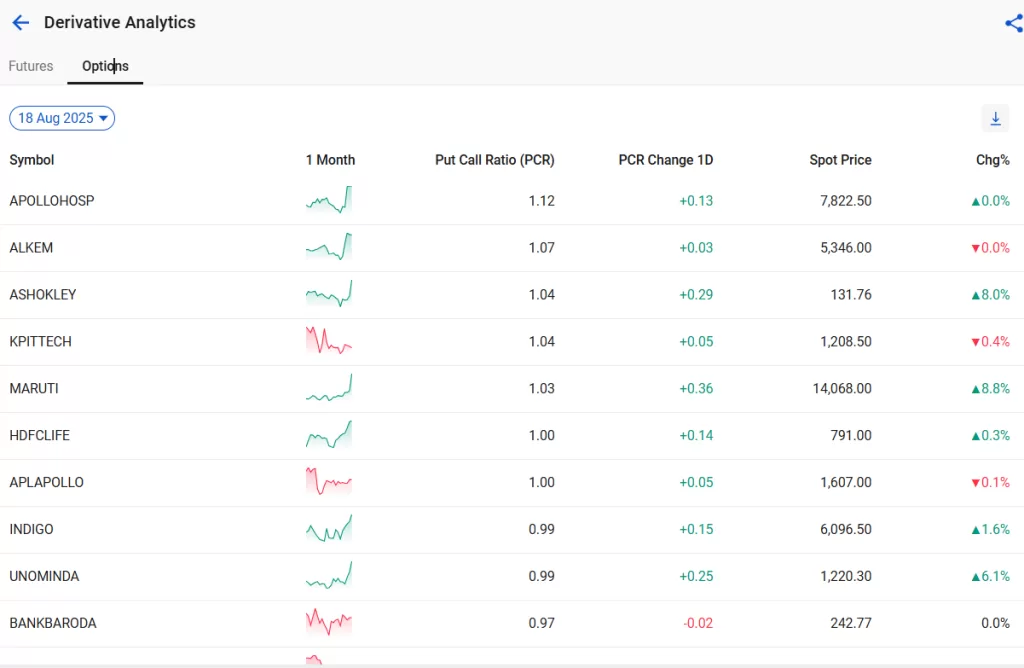
The above images are screenshots from the Derivative Analytic section of the StockEdge app. It shows the list of F&O stocks along with their lot size and their trend in open interest, which can help you understand whether the stock is bullish or bearish. Additionally, for options, we have a separate tab that shows the trend in PCR (Put to Call Ratio) of a stock along with daily change in PCR that can also help you figure out whether the stock is overbought or oversold.
If all these seem confusing to you, then do read our previous blog: Derivative Analytics: Unlock the Power of Derivatives to analyze Stocks!
Basic Options Trading Strategies
An option strategy involving buying and selling call and put options simultaneously is a way to navigate the ups and downs of the stock market by using a combination of different options to manage risks and potential profits.
To be honest, there is no limitation on how you can create option trading strategies. Buying or selling options can also be done in combination with your holding of stocks in your portfolio.
For instance, imagine you are holding 3000 shares of SBI at 600 per share. However, due to uncertainty in the broader market, you are anticipating a downside risk on SBI. You can simply buy a put option contract to hedge your long position in SBI stock. This is called a Protective Put or Married Put strategy. This strategy acts as insurance, limiting losses if the asset’s price falls.
Also, there is another way you can hedge your long position in a stock. Sell an OTM call when you anticipate that the upside in the stock is limited. This way, you, as an option seller, will receive the premium that generates income from existing stock holdings. It is considered a conservative strategy.
If all these seem complex, let’s start with a few basic option trading strategies:
Long Call Strategy
In the Long Call strategy, you purchase a call option anticipating the uptrend of the underlying asset. By acquiring the call option, you gain the right to purchase the asset at a set price before the option expires. The goal is to profit from the anticipated rise in the asset’s value. If the market moves in your favor, you have the choice to either exercise the call option or sell it for a profit.
Take a look at the pay-off, when you buy a strike of 5000 by paying a premium of ₹70.
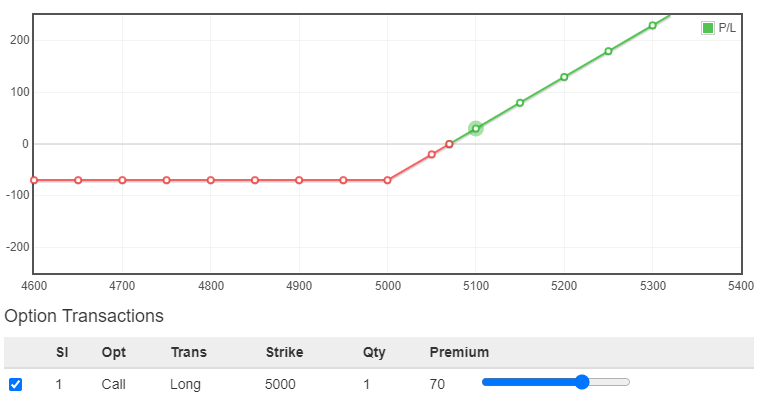
You can see the maximum loss is the premium you have paid, and you will start earning when the underlying asset goes above 5070. How? That’s because (5000+70) which is the breakeven point and will earn profit if price goes above break-even.
Long Put Strategy
In the Long Put strategy, you acquire a put option, expecting the underlying asset’s price to drop. By obtaining the put option, you secure the right to sell the asset at a set price before the option expires. The goal is to profit from the anticipated decrease in the asset’s value. If the market moves as expected, you have the option to either exercise the put option or sell it for a profit.
Let’s take a simple example with buying a put of 5000 paying a premium of ₹70.
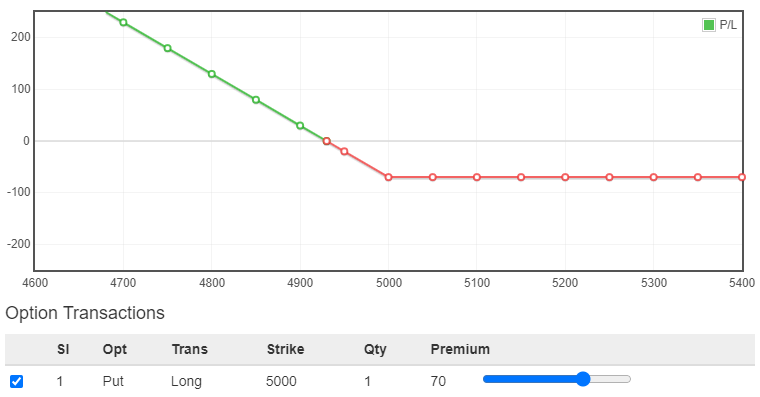
As you can see, the graph turned upside down from Long Call, as you are anticipating a downside move. When price goes below (5000-70) = 4930 which is the breakeven point, you will start earning profit.
To learn more advanced option trading strategies, you can visit elearnoptions
Advantages and Risks in Options Trading
Everything has its own advantages and disadvantages, and so does option trading. You must carefully understand the potential rewards and risks before engaging in the derivatives market. First, advantages you will get when you are trading in options.
Potential Benefits of Options Trading
- Leverage: Options allow you to take a larger position on an underlying asset with a smaller amount of capital (premium). This potential for leverage can amplify returns.
- Flexibility: Options provide a wide range of strategies to accommodate various market conditions. You can take positions based on expectations of price movements, volatility, or even lack of movement.
- Risk Management: Options can be used to hedge and manage risk. Strategies like protective puts or covered calls, as mentioned earlier, allow you to limit potential losses and protect your portfolio from adverse market movements.
- Income Generation: Selling options, such as covered calls, can generate income through the collection of premiums.
What are the Risks Involved in Options Trading?
Now, let’s understand some of the risks associated with option trading.
- Limited Time: Options have expiry dates. If the anticipated price movement doesn’t occur before the export of the contract, the option may expire worthless, leading to a loss of the premium paid.
- Potential for Losses: While leverage can magnify gains, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against the option holder, the losses can exceed the initial investment.
- Market Risk: Options are heavily influenced by the price movements of the underlying asset. Market volatility, unexpected news, or changes in economic conditions can impact option prices.
- Obligation Risk: If you are a seller of options, there’s a risk of obligation. When the buyer wishes to exercise the option, you may be obligated to buy or sell the underlying asset at the agreed-upon price, which might not be favorable.
How do you trade in options?
Options trading involves buying or selling call or put options, giving the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before expiration.
Is option trading a good investment?
It can be for experienced investors, offering opportunities for leverage and risk management, but it comes with complexities and risks.
Is trading in options profitable?
It can be profitable, but success depends on knowledge, strategy, and market conditions; losses are possible.
How Much Money Do You Need to Trade Options?
The amount varies, but a common guideline is to start with a few lakhs; more capital allows for diversified strategies.
What are the 4 types of trading?
The four main types are day trading, swing trading, position trading, and scalping, each with its own time horizon and approach.











