Table of Contents
Beating LIC’s mammoth IPO worth Rs 20,557 crore in May 2022, Korean car manufacturer Hyundai Motor India’s IPO of Rs 27,856 crore will rewrite record books as India’s largest public issue ever.
However, in the wake of LIC’s underwhelming performance, investors are understandably wary.
Will Hyundai’s IPO be yet another instance of overhyped potential that ultimately falls short of expectations, or could it emerge as a lucrative opportunity for both short-term profits and long-term growth?
Let’s delve into the company’s details, financial performance, and other details, which give you the confidence to apply for the initial public offering by the company. Also, it is essential to remember that not all initial public offerings (IPOs) come with a promise of equal profits, so in today’s blog, let’s analyze some key factors of Hyundai Motor India Limited on the IPO before you apply!
Hyundai Motor India Limited IPO is open for subscription from (15th Oct, 2024) today onwards!
Hyundai Motor India IPO Details:
- IPO Open Date 15th October 2024, Tuesday
- IPO Close Date 17th October 2024, Thursday
- Price Band ₹1865 to ₹1960 per share
- Lot Size 7 shares
- Face Value ₹10 per share
- Issue Size at upper price band ₹27870 cr (Offer For Sale ₹27870 Cr)
- Listing exchanges NSE, BSE
- Cut-off time for UPI mandate confirmation by 5 PM on October 17, 2024
The tentative timeline for the Hyundai Motor IPO is as follows:
- Basis of Allotment 18th October 2024, Friday
- Initiation of Refunds (if not allotted) 21st October 2024, Monday
- Credit of Shares to Demat (if gets allotments of shares) 21st October 2024, Monday
- Listing Date 22nd October 2023, Tuesday
About the Company
Before subscribing to the Hyundai Motor India IPO, let’s understand how this company works.
Hyundai Motor India Limited, incorporated in May 1996, is part of the Hyundai Motor Company, which is the third largest auto original equipment manufacturer (OEM) in the world based on passenger vehicle (PV) sales. It is primarily involved in manufacturing and selling four-wheeler PVs and parts, such as transmissions and engines, in India and abroad.
Its portfolio includes 13 models across multiple PV segments, including sedans, hatchbacks, sports-utility vehicles (SUVs), and battery electric vehicles (EVs).
- Sedans: These cars are known for their luxury, performance, and safety. They often have a quieter cabin than other vehicles, and some offer features like heated seats and adjustable lumbar support. Sedans are also good for storing valuables safely, as the trunk is isolated from the passenger compartment. Notable models from Hyundai Motor India include the Aura and Verna.
- Hatchbacks: These smaller cars are known for their fuel efficiency and versatility. They have a trunk located behind the rear passenger seats, and the rear seats can be folded down to create more space. Hatchbacks are usually cheaper than SUVs, and they have smaller tyres, which are less expensive to replace. Popular Hyundai hatchback models include the Hyundai i20, Hyundai Grand i10 NIOS, and Hyundai i20 N Line.
- SUVs: These cars are known for their cargo space and off-road capabilities. They have an open cabin and cargo space design, similar to hatchbacks, but typically on a larger scale. Hyundai’s SUV range includes the Exter, Venue, Creta, Venue N Line, and Alcazar.
- EVs: Electric vehicles have unique features like regenerative braking, which allows the car to create electricity as it decelerates. This means that a carefully driven EV can theoretically be driven without touching the brake pedal. A notable model in Hyundai’s EV lineup is the IONIQ 5.
It has 2 manufacturing plants located in Chennai (Tamil Nadu) with a total production capacity of 8,11,000 units in FY24. As on 30th June 2024, it had 1,377 sales outlets across 1,036 cities and towns in India. It has an agreement to pay 3.5% to Hyundai Motor Company as royalty in connection to sales arising from PV or parts.
Exporting to over 150 countries, including Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia, it serves as Hyundai Motor Company’s production and export hub for emerging markets, with a focus on models like Verna and Venue.
As part of its premiumization strategy, the company shifted its vehicle portfolio toward higher ASP models like SUVs, resulting in an ASP increase from ₹6,69,455 per unit in FY21 to ₹7,71,840 per unit in FY24. However, in Q1 FY25, ASP fell to ₹7,74,574 from ₹7,91,805 in Q1 FY24, primarily due to a decline in large SUV sales as customers awaited the Alcazar facelift set for September 2024. Additionally, premium sedan sales dropped, unlike in Q1 FY24, when strong demand for the newly launched Verna boosted ASP.
Auto Sector Outlook in India
Domestic passenger vehicle industry is an oligopolistic market with few players dominating the entire industry. Maruti Suzuki leads the PV industry in terms of domestic sales volumes. Hyundai Motor India is the second largest contributor to the domestic sales, followed by Tata Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra. These 4 players together contribute approximately 80% of the market.
Between Fiscals 2019 and 2024, India’s domestic PV sales volume rose at 5% CAGR. This growth was despite the sales contraction (at 10% CAGR) witnessed during Fiscals 2019 to 2021. From the low base of Fiscal 2021, PV sales bounced back and grew at a healthy pace to reach a historic high of 4.2 million vehicles in Fiscal 2024.
The passenger vehicle industry is usually classified based on body types into hatchbacks, sedans, SUVs, MPVs, and vans.
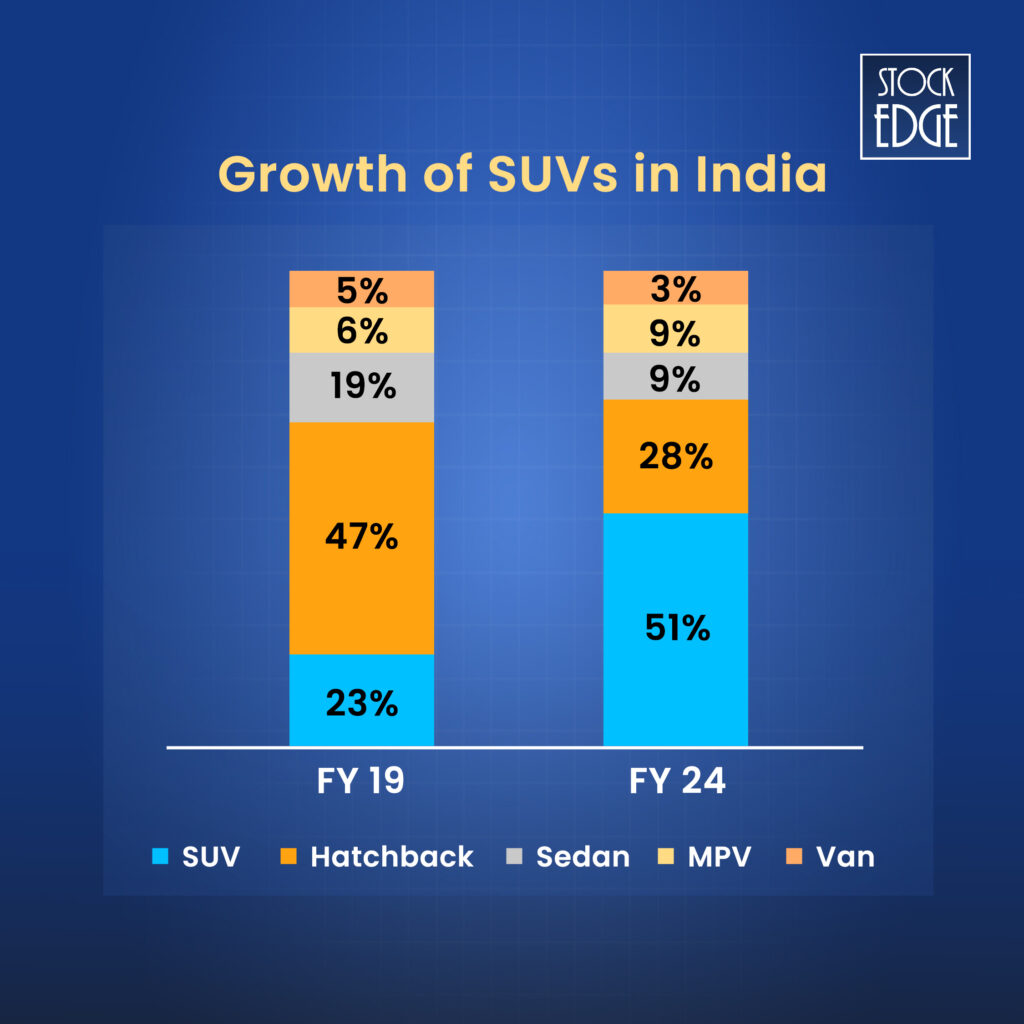
The share of small cars (hatchbacks) reduced from 46.9% in Fiscal 2019 to 27.7% in Fiscal 2024. During the same period, the share of SUVs increased from 23.2% in Fiscal 2019 to 51.2% in Fiscal 2024.
The global PV volume sales in CY23 stood at 6.53 cr units v/s 6.48 cr units in CY19. Between CY19 and CY23, the industry witnessed a CAGR of 0.2%. Globally, in CY23, Toyota Group dominated the PV sales (with sales of ~1.1 cr cars), followed by Volkswagen Group with sales of 0.9 cr cars. Hyundai Motor Group (including Hyundai and Kia) took the third position, recording sales of 0.7 cr cars.
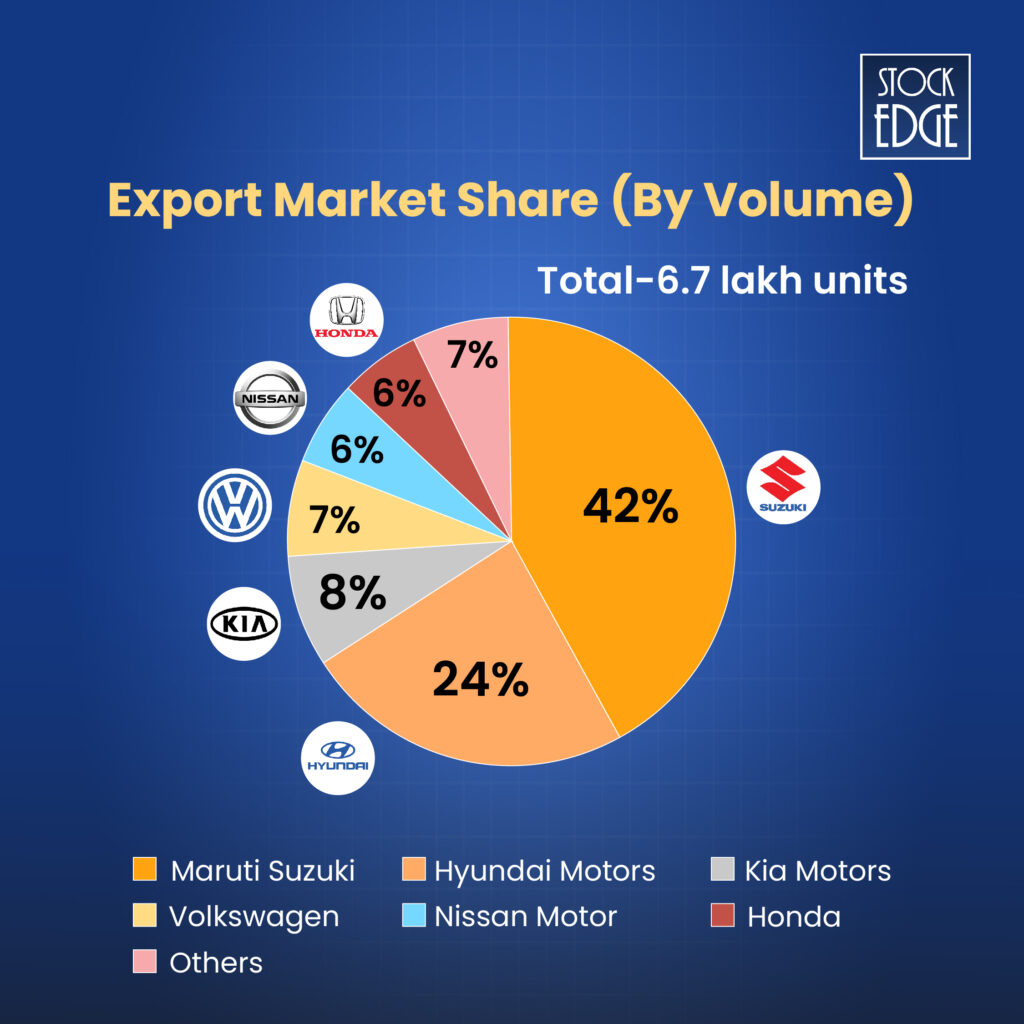
The Indian PV industry registered a sales volume (domestic) of ~42 lakh units in FY24, up from ~33 lakh units in FY19. The export volume reached 6.7 lakh units in FY24, up from 6.8 lakh units in FY19.
Financial Performance
Since its inception, Hyundai has consistently grown stronger and has been one of the most recognised brands in India. It has also been the first mover in various PV categories.
The company’s revenue has steadily grown, increasing from ₹47,378 crores in 2022 to ₹69,829 crores in 2024, and it stands at ₹17,344 crores as of June 30, 2024. Sales volumes for both domestic and export markets increased from 2022 to 2024. Domestic sales grew from 4,81,500 units in 2022 to 6,14,721 units in 2024. Export sales rose from 1,29,260 units in 2022 to 1,63,155 units in 2024. They also expanded its sales and service outlets, with the number of sales outlets increasing from 1,282 in 2022 to 1,363 in 2024 and service outlets growing from 1,422 to 1,549.
Now, let’s examine the key fundamental parameters of the Hyundai Motor India IPO and how it compares with its peer companies in this competitive landscape.
Hyundai’s revenue of ₹69,829 crores is also the lowest among the four companies, with Maruti Suzuki and Tata Motors far ahead in this metric. Despite these lower figures, Hyundai shows strength in sales volume, with 7,77,876 units sold, making it the second-largest after Maruti Suzuki, which sold 21,35,323 units. Hyundai’s P/E ratio of 26.28x is close to Maruti’s, reflecting similar investor confidence, though Tata Motors is valued lower at 10.15x.
In summary, Hyundai stands out for its strong sales volume and profitability margins. However, it trails behind in overall size and market reach compared to its larger competitors, especially Maruti Suzuki.
Now let’s understand the objective of the Hyundai Motor India IPO.
Objectives of the Issue
The objective of the Hyundai Motor India IPO is to raise Rs 27,856 crore, which includes an offer-for-sale of 14.2 crore shares, representing a 17.5% stake in the company.
The company will not receive any proceeds from the Offer (the “Offer Proceeds”), and the Promoter Selling Shareholder will receive all the Offer Proceeds after deduction of Offer-related expenses and relevant taxes, which the Promoter Selling Shareholder will bear.
Let’s understand the risk factors of the Hyundai Motor India IPO
Risk Factors
Here are the risks that are highlighted for Hyundai Motor India IPO:
- The company’s operation is highly dependent on the continued availability of parts and materials. The total cost of material consumed accounted for ~72% of the total income in FY24.
- Its group company, Mobis India Limited, supplies modular parts used in the manufacturing process of passenger vehicles and parts. These parts constituted 18% of the total parts and materials supplied in Q1 FY25. Hence, the company faces the risk of suppliers failing to provide parts and materials on time or at all.
- It is dependent on suppliers outside India to source raw materials. In FY24, it sourced ~22% of its total purchase of parts and materials from outside India.
- It operates in a highly competitive and fast-evolving market, with Maruti Suzuki leading the PV market. In the export market, its competitors are Maruti Suzuki India, Kia Motors, Volkswagen, Nissan Motor, and Honda Cars India.
- The company paid a special dividend of ₹10,782 cr to its promoters in FY24 and the ability to utilize internal accruals and cash & bank balances to invest in the business has been reduced, as a result, borrowings may be required for future expansion plans, leading to increased borrowing costs that could affect profitability, going forward.
- As per the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Rules (SCRR), the company is required to increase its public shareholding to 25% within 5 years from the date of listing. Until full compliance with this minimum public shareholding requirement is achieved, public shareholders may not benefit from the additional public float.
Should you subscribe to the Hyundai Motor India IPO?
The automobile sector’s share of the national GDP increased from 2.77% in 1992–1993 to around 7.1% presently. In April-June FY25, the total production of passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, three-wheelers, two-wheelers, and quadricycles was 75,48,668 units. The Indian automotive industry is expected to reach US $300 billion by 2026.
To have a clear understanding of the potential risks and rewards associated with an investment is crucial prior to getting involved. Thus, in this blog, we have provided in-depth insights into both the opportunities and potential drawbacks linked to investing in the Hyundai Motor India IPO. Our experts at StockEdge have assigned a favourable rating to this IPO and have compiled a comprehensive IPO Note. This IPO note delves into the company’s financial status and includes a SWOT analysis, offering readers enhanced insight into the company’s future prospects, ultimately aiding informed investment choices.
Investments in IPOs have been rewarding for many investors in recent years. Our previous blog on Northern ARC Capital’s IPO, in which our team had given an average IPO rating, reported a listing gain of nearly 33% above its issue price.
StockEdge has a separate section on IPOs under the Explore tab, where you can see a list of upcoming, ongoing, and recently listed IPOs.
Join StockEdge Club, where our team of research analysts will be dedicated to solving your queries related to investments, trading, or IPOs.
Happy investing!