Table of Contents
In today’s world, every parent desires to give their children the best and highest-quality education, whether in India or abroad. Good education is a pillar to the development of a child’s overall personality and the career opportunities it opens for an individual. When we talk about school education, such costs are not as hefty as costs for higher education.
There can also be a need for other financial goals such as weddings, goals like planning a vacation or buying a new car, or it can be saving to gift your special one.
In order to meet expenses for your financial goals, it is important to understand- Can a minor invest in mutual funds?
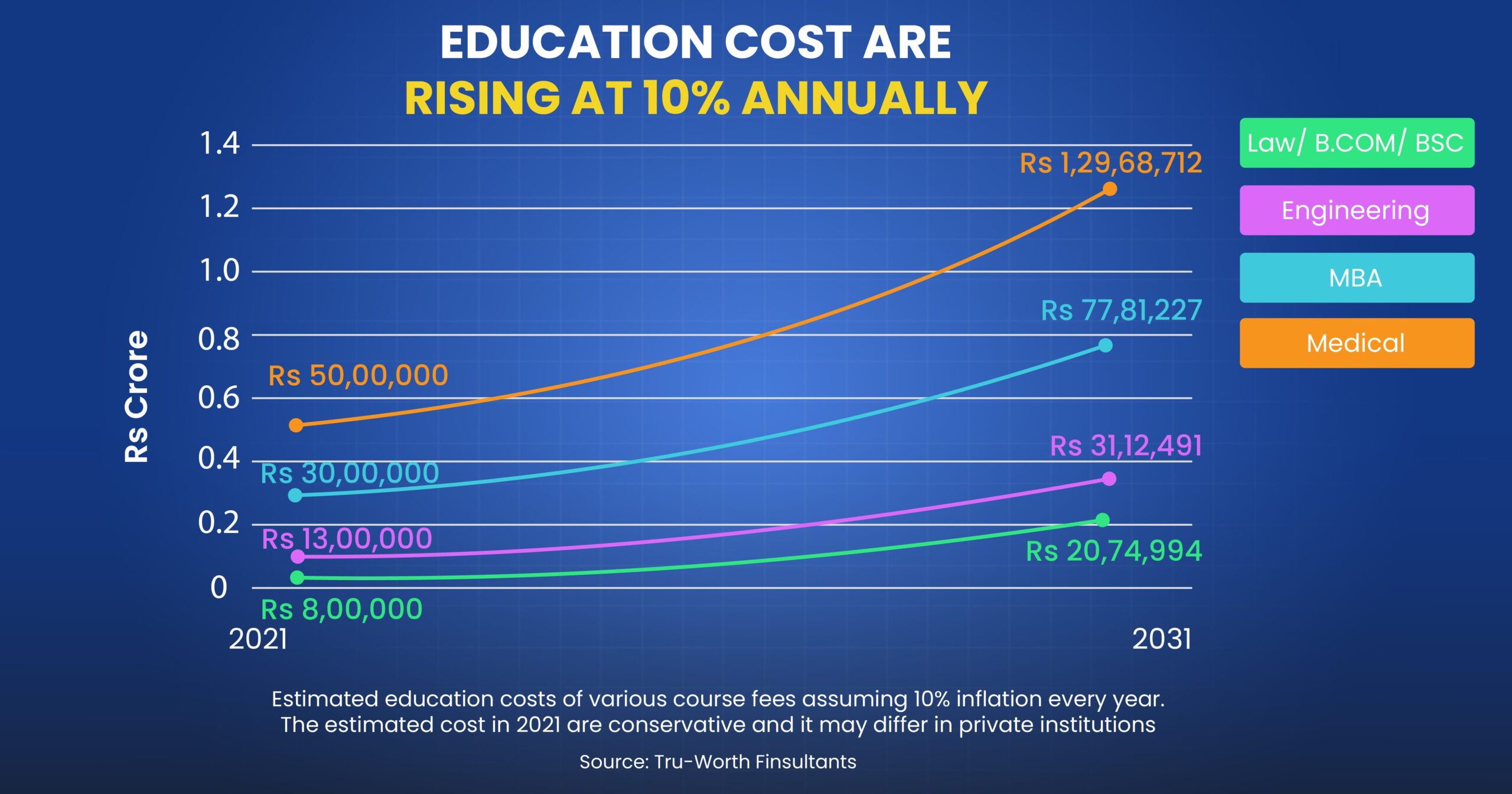
The cost of higher education is relatively high, and it keeps on increasing with time, as shown in the above image. Currently, there are numerous career options and education streams to choose from, and the cost to pursue a career can differ by huge margins.
Hence, accumulating a sufficient corpus for higher education or any specific goal plays a crucial part in financial planning for all parents. The need for such a corpus can occur at any point in time.
Therefore, long-term financial planning should begin from the first day when it comes to planning for a family. An ideal strategy would be to start investing in your child’s name from a young age, preferably within a few years of their birth.
The “Power of Compounding” is considered the 8th wonder of the world. Two main pillars of compounding are starting to invest early and investing regularly.
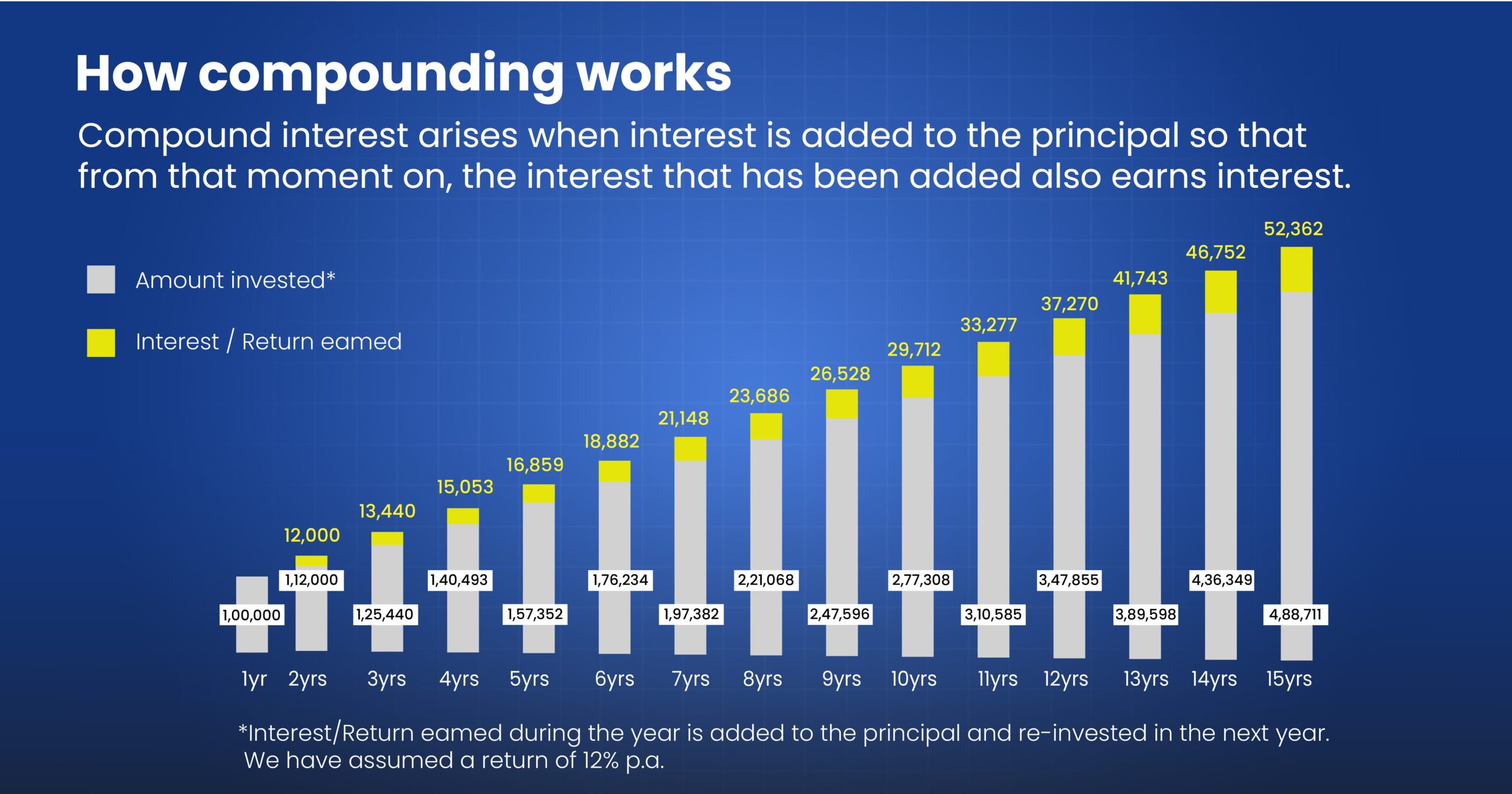
Parents should even encourage their children to start investing early and to develop a habit of savings, which will help them fulfill their future desires and meet their financial goals. As shown above the power of compounding works like a magic, Rs. 1 lakh invested will be worth 4.88 lakhs in just 1 years (assuming Return of 12% p.a.)
But is it possible for minors to invest? Or should their parents invest in their minor’s name?
In this blog, we will learn how to start investing in the name of a minor and what procedures are required to ensure secure investments.
Who is a “Minor”?
The first question that comes to one’s mind is, “Who really is a minor?”
It is necessary to understand who is considered a minor under Indian law. A minor is a person who has not attained the age of majority.
In India, according to the Indian Majority Act of 1875, a minor is an individual whose legal age is below 18 years of age.
How can Minors invest in Mutual Funds Or Stocks?
The answer is yes. Minors can invest in stocks and mutual funds, but there is a twist: They can’t do it directly.
Investments can be made by parents or a legal guardian who holds authority over the investment and oversees the demat accounts, trading accounts, or mutual fund folios in the name of a minor. They act as custodians of the account for minors.
As per the Indian Contract Act of 1872, minors are incompetent to hold any form of contract.
According to the act, in order to be competent and to invest,
– the person should be of the age of majority, which in India is 18 years.
– he should be of sound mind at the time of making the contract.
– he should not be disqualified from contracting by any law to which he is subject.
Investing can be a helpful financial tool as parents can plan and invest on behalf of their child.
One key reason is Inflation. Only saving money but not investing can eat up the wealth and decrease the purchasing power of money.
In India, Inflation is 5%to 7%, but when we talk about Inflation for food, healthcare and education, it is even higher.
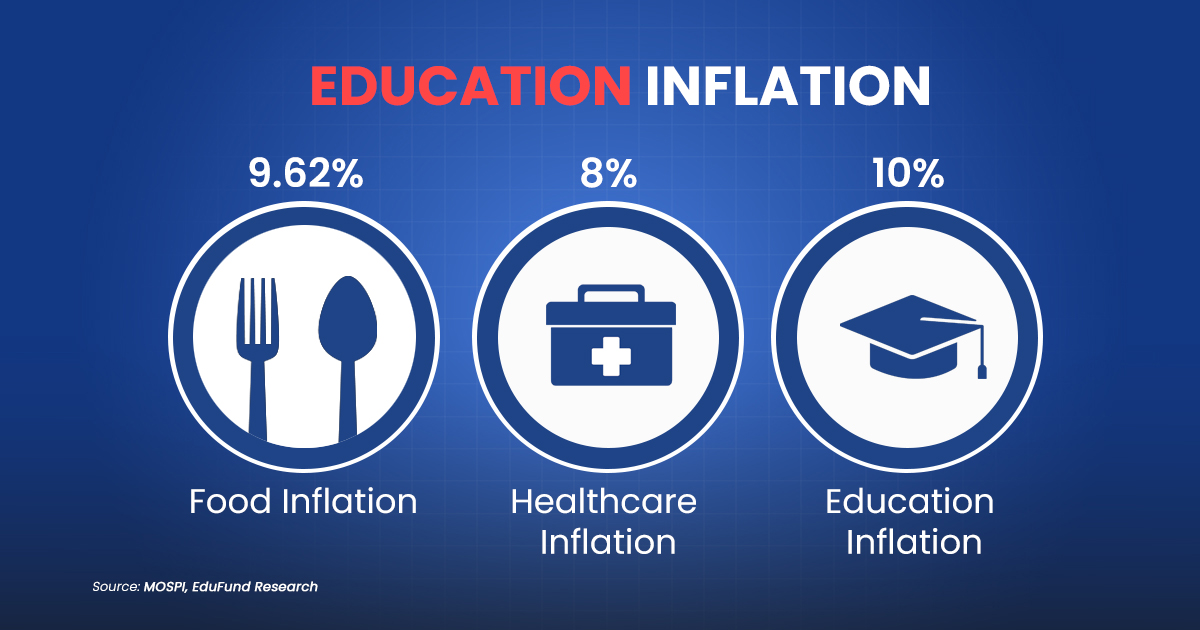
What is the Procedure for Investment as a Minor?
The real question that arises in your mind must be how to actually start and what procedures need to be followed to start investments for a minor.
There are better ways to begin the investments than opening a trading account in the name of the minor. To invest in stocks or mutual funds for minors, a few points to keep in mind:
Application to Stockbroker: An official application must be made to the stock broker stating basic details such as contact details, email ID, address details, date of birth etc.
Proof of Age: The birth certificates of minors must be submitted to confirm the children’s age. It shall be below 18 to follow the next steps.
Appointing a guardian or a parent: As the minor is incompetent to make decisions, the parents/guardian need to manage all the investments. A document declaring the relationship between the minor and guardian/parents is required.
KYC and banking information: The KYC of both parents and the minor needs to be submitted, along with the PAN card details and banking details. KYC documents generally have both address proof and photo identity proof for verification.
No Nominees or Joint Account: The new account created should not have any nominees or a joint account holder.
What are the documents required for Investing in the name of a Minor?
We have understood about the procedure for investing by a minor, let us see the documents which are required to
The following documents are required to for investment in the name of minor:
- A valid birth certificate, as proof of the minor’s age
- Minor’s mark sheet is required
- KYC documentation such as Aadhar card and PAN card must be provided by the parent/guardian.
- An application form is to be submitted naming the minor as the beneficial owner.
- A guardianship certificate which is certified by the court as evidence of the guardian’s relationship with the minor.
These documents are mandatory to open a minor’s mutual fund account, ensuring regulatory compliance and transparent investment in mutual funds for minors.
Other Investment Options available for Minors
Apart from investments in mutual funds/stocks by a minor, there are other investment avenues to consider when investing for a minor. Let us understand can minors invest in other means of investment.
Gold: A minor can invest in Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs), but only with the help of a guardian. The guardian is then required to submit the SGB application along with the PAN details to subscribe in the issue.
Bank Fixed Deposits: Under the Fixed Deposit schemes for children, the parents or guardians can open an account on behalf of the minor. They can withdraw the money upon the fixed deposit maturing or the minor reaching the legal age of 18.
Real Estate: A minor can invest in real estate by entering into a contract with another adult through its legal guardian, with all documents duly signed on behalf of the minor. This is generally not that widely used as an investment option due to high ticket size of investments.
Public Provident Fund (PPF): A guardian can open a PPF account in the name of his minor child. However, the guardian and the minor can only invest a maximum of INR 1.5 lakhs per year.
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY): These schemes focus on saving for a girl child, where a legal guardian or a parent can hold two accounts simultaneously for a minor girl child.
The Sukanya Samriddhi Account matures when the beneficiary reaches the age of 21. However, parents can withdraw a maximum of 50% of the account balance to finance higher education.
Pros and Cons of Investing in a Mutual Fund in a Minor’s Name
PROS
- Early Investing: Starting to invest early on facilitates more significant potential for wealth creation by the power of compounding.
- Better Financial Planning: Investing in a minor’s account makes a parent prioritize their child’s future and not withdraw the investment made for their other needs.
- Encourage Financial freedom: It will help teach a minor to be more financially responsible from an early age.
CONS
- When the minor turns 18 and assumes control of the mutual fund invested, they may need to gain the financial knowledge or responsibility to handle the money invested for their future.
- The guardian controls the fund, which does not provide the minor with the necessary knowledge they need.
- Some investment avenues are limited to adults, which may prevent minors from building diversified portfolios.
Procedure to be followed after the Minor Child attains Adulthood
Once a child attains the age of 18 and becomes a major, the guardian must submit a written application with the minor’s signature requesting a change of status from minor to major; otherwise, all transactions will be stopped in the account.
For minors to invest in mutual funds, KYC needs to be submitted again after minor completing 18 years of age, along with submission of new signature by minor, which will be replaced by the guardian’s signature. PAN Card details and bank account details should also be submitted to the AMC.
Thus, now the child will be liable to handle all the investments and they will become the account holder. Additionally all the tax implications now will be fulfilled by the child after he becomes a major.
Taxation
The most important thing that investors look out for is how the taxation will be in case a minor invests in a mutual fund scheme. Till the child is a minor, any capital gains are taxed according to the guardian’s income tax slab until the minor turns 18, after which the burden of tax falls on the minor.
After the minor attains the age of 18, the fund will follow equity taxation rates, i.e., long-term capital gains tax (LTCG) will be charged at 10% after 12 months of holdings, and holdings less than 12 months will attract short-term capital gains tax (STCG) at a flat 15%.
Under section 80C, gains upto 1 lakh are exempt from taxation for investments made above 12 months. It encourages investors to invest for a long-term horizon, focusing on disciplined investing.
Top Recommended Mutual Funds
SBI Conservative Hybrid Direct Fund
This is a Conservative Hybrid Fund which invests minimum 75% in debt instruments protecting your capital and focusing on steady income. It invests remaining in equity instruments for potential capital appreciation.
This mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 11.90% in the last five years and 10.66% in the last ten years.
Kotak Debt Hybrid Fund
This is also a Conservative Hybrid fund category fund. In the last five years, this mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 13.08% and 11.43% in the last ten years.
ICICI Prudential Regular Savings Fund
This is also a Conservative Hybrid fund category fund. In the last five years, this mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 10.77% and 10.76% in the previous ten years.
HDFC Balanced Advantage Fund
This is a Balanced Hybrid Fund with a focus on both equities and debt in a blanched way. For a comparatively higher risk-taker this fund is promising for long-term investing.
This mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 20.16% in the last five years and 15.45% in the last ten years.
ICICI Pru Equity & Debt Fund- Direct Plan
This fund is an Aggressive Hybrid Fund that focuses on a minimum of 65% in equity securities and the remaining in debt instruments. In the last five years, this mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 22.29% and 17.41% in the last ten years.
ICICI Pru Multi Asset Allocation Fund
This is a Dynamic allocation fund that focuses on more than 2 asset classes. It mitigates risk by investing in multi-assets like equity, debt, gold and silver, real estate, REITs, etc.
This mutual fund scheme has delivered annual returns of 21.23% in the last five years and 15.73% in the last ten years.
Conclusion:
Education inflation, food inflation and healthcare inflation in India pose a significant financial burden on families, making it difficult for parents to ensure that their children receive a quality education and lifestyle.
However, emphasizing early investing and taking proactive steps towards disciplined investing can ensure that children’s, when grown up, can fulfill all their desires and aspirations.
Meeting the financial needs of an individual requires financial planning. Though, as we spoke about different investment product to accumulate money for future purpose, mutual funds provide higher growth and flexibility in approach.
Parents can help their children to achieve their career goals without sacrificing their financial stability. By taking steps to manage the cost of education, families can ensure that their children receive a quality education and lifestyle without sacrificing their financial future.
To summarize, the best way to invest for minors is by investing in mutual fund schemes through a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP), which will empower minors when they become 18 years of age. At the same time, guardians/ parents looking to secure the future of their children should focus on investing in the name of a minor for a minimum of 10 to 12 years till they turn 18, which in turn will encourage financial independence and a sense of security for the child’s future.










